Drug safety in menopause is the key consideration for women undergoing this natural transition. For most, it begins in their late 40s to early 50s, with the average age being around 51. However, every woman’s journey is unique, and some may experience early menopause in their 30s or 40s due to genetics, medical treatments, or certain health conditions. While this biological phase is a normal part of aging, it often brings challenges such as hot flashes, dryness, and mood swings, which can feel overwhelming at times. It’s important to remember that these experiences are completely normal—and the good news is, you don’t have to worry as much
Knowing about which medications to take can make a significant difference in how comfortable and supported you feel during this transition. This blog will guide you through everything you need to know about drug safety in menopause, from common treatments to practical advice on staying informed and making the best choices for your health.
What Exactly is Menopause and Why Does it Occur?
Menopause is a stage in a woman’s life that signals the end of her menstrual cycles and fertility. On the bright side, it means you no longer have to deal with painful period cramps. A woman is considered to have reached menopause when she has gone 12 months without menstruating. This occurs because the ovaries stop producing eggs, leading to a decrease in key hormones like estrogen and progesterone. The resulting hormonal shift brings an end to menstruation and can cause a range of physical and emotional symptoms.
Menopause unfolds in stages, and each stage comes with its own set of symptoms.
These stages include:
- Perimenopause: This phase before menopause can last for several years. During this time, hormone levels can shift, causing irregular periods, hot flashes, mood swings, and other symptoms.
- Menopause: The point when a woman has not had a period for 12 consecutive months leads to menopause.
- Post menopause: It occurs after menopause, when symptoms like hot flashes may subside, but the risks for certain health issues, such as osteoporosis and heart disease, increase due to lower estrogen levels.
Drug Safety in Menopause: How to take Meds Safely
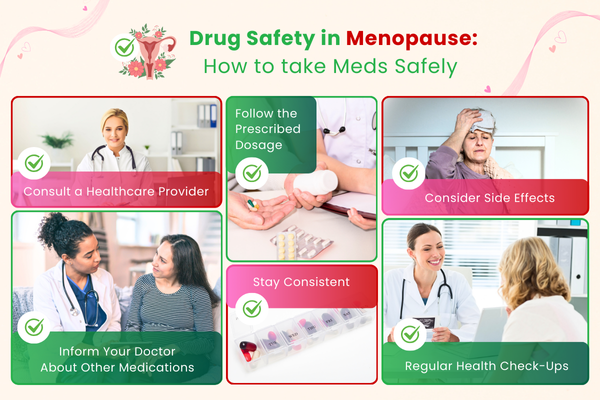
Navigating menopause can be a challenging! Taking the right steps to ensure drug safety in menopause not only helps improve your quality of life but also prevents potential health risks. Here are some important guidelines to follow for safely taking medications during this phase.
- Consult a Healthcare Provider: Before starting any medication, it’s crucial to consult with a doctor to understand the options available. Medications like hormone replacement therapy (HRT) or non-hormonal treatments may be recommended depending on your symptoms.
- Follow the Prescribed Dosage: Always take medications as prescribed. Do not alter the dosage or frequency without consulting your doctor, as this could affect the effectiveness or cause unwanted side effects.
- Consider Side Effects: Understand the potential side effects of the medication you’re taking, whether it’s for hot flashes, sleep issues, mood changes, or osteoporosis. Be aware of any adverse effects and report them to your doctor for drug safety in menopause.
- Stay Consistent: To support drug safety in menopause, take medications at the same time each day to avoid missing doses. Consider setting reminders if it helps.
- Inform Your Doctor About Other Medications: If you’re taking any other medications, herbal supplements, or vitamins, make sure your doctor is aware to avoid any interactions.
- Regular Health Check-Ups: Regularly visit your healthcare provider to monitor the effectiveness of the medications and adjust them if necessary.
Drug Safety in Menopause: Medications for Symptom Relief
While lifestyle changes, diet, and exercise can help alleviate some symptoms, it is also important to prioritize drug safety in menopause for relief. Here are some of the most common medications used during this time:
| Medication | Purpose | Common Examples | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) | HRT Relieves hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness | Estrogen-only pill (Cenestin), Combined estrogen-progesterone pill (Activella) | Highly effective for hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness. | Not advised for women with certain health conditions. |
| Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) | Treats hot flashes and mood swings | Fluoxetine (Prozac), Sertraline (Zoloft), Paroxetine (Paxil) | Helps with both mood swings and hot flashes. | Can cause nausea, sexual side effects, weight gain, and sleep problems. |
| Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs) | Helps with osteoporosis, mimics estrogen in some tissues | Raloxifene (Evista), Tamoxifen (Nolvadex) | Good for bone health and reducing breast cancer risks. | May raise the risk of blood clots and hot flashes. |
| Gabapentin | Reduces hot flashes | Gralise, Neurontin | Useful for women who can’t take estrogen. | Drowsiness, dizziness, weight gain, and potential memory issues. |
| Vaginal Estrogen | Treats vaginal dryness and irritation | Estrace, Vagifem, Estring | Targets only vaginal symptoms with minimal systemic effects. | Can still have mild systemic effects and isn’t suitable for women with certain health risks, such as a history of breast cancer. |
| Progestins | Reduces endometrial cancer risk and controls symptoms | Medroxyprogesterone (Provera) | Reduces risk of uterine cancer in women using estrogen. | Can cause mood swings, bloating, weight gain, and irregular bleeding. |
| Over-the-counter Remedies | Alleviate mild symptoms like hot flashes | Black Cohosh, Soy Isoflavones, Vitamin E | Natural alternatives with fewer side effects. | Limited evidence of effectiveness, potential interactions with other medications, and may not work for all women. |
Note: This table offers an overview of common options for drug safety in menopause, but treatment should always be individualized in consultation with a healthcare provider.
Managing Drug Safety in Menopause: Essential Interactions
When managing medications, it’s essential to be aware about the drug safety in menopause. Drug interactions can impact the effectiveness of treatment or even cause harmful side effects. This is especially important during menopause, as many women take multiple medications to manage their symptoms.
Here are some key considerations regarding drug safety in menopause:
1. Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) Interactions
HRT is commonly prescribed to manage symptoms like hot flashes and vaginal dryness. When considering drug safety in menopause, it’s crucial to be aware of potential interactions such as with:
- Antidepressants (SSRIs/SNRIs): These can affect estrogen metabolism, potentially reducing the effectiveness of HRT or causing side effects like nausea or sexual dysfunction.
- Blood Thinners (Anticoagulants): Estrogen can increase the risk of blood clotting, and when combined with blood thinners like warfarin, there may be an increased risk of bleeding or clotting complications.
2. Antidepressants and Mood Stabilizers
SSRIs and SNRIs are commonly prescribed for mood swings, depression, and anxiety during menopause. To maintain drug safety in menopause, it’s important to consider their potential interactions with:
- Pain Medications (NSAIDs): Taking these antidepressants with NSAIDs like ibuprofen or aspirin can increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Blood Pressure Medications: Certain antidepressants can lower blood pressure, especially when combined with antihypertensive drugs, leading to dizziness or fainting.
3. Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs)
SERMs like raloxifene, commonly used for osteoporosis, naturally mimic estrogen’s effects in specific tissues. Ensuring drug safety in menopause is vital, as these medications can interact with:
- Blood Thinners: SERMs can increase the risk of blood clots, especially when combined with anticoagulants like warfarin.
- Cholesterol Medications (Statins): Some studies suggest that SERMs may interfere with the action of statins, which are used to manage high cholesterol levels.
4. Gabapentin
Gabapentin is commonly prescribed to manage hot flashes during menopause, but its interactions with other medications should be carefully considered for drug safety in menopause. These include:
- Antidepressants: Combining gabapentin with antidepressants or sedatives may increase drowsiness, dizziness, or the risk of memory issues.
- Pain Medications: When combined with opioid pain medications, gabapentin may increase sedation and the risk of respiratory depression.
5. Vaginal Estrogen
Vaginal estrogen treatments are typically used for vaginal dryness and irritation. Though it is a localized treatment, drug safety in menopause still requires awareness of interactions with meds such as:
- Antifungal Medications: Drugs like fluconazole can increase estrogen levels in the bloodstream, which may result in side effects like breast tenderness or bloating.
- Antibiotics: Certain antibiotics, such as rifampin, may lower the effectiveness of vaginal estrogen by accelerating its breakdown.
6. Progestins Interactions
Progestins are often used in combination with estrogen in hormone replacement therapy (HRT) to balance the effects of estrogen and protect the uterus. However, they can interact with other drugs, such as:
- Anticonvulsants: Medications like phenytoin, carbamazepine, or phenobarbital can decrease the effectiveness of progestins by speeding up their metabolism, which may result in breakthrough bleeding or unintended pregnancy if used for contraception.
- Antibiotics: Certain antibiotics, especially rifampin, may reduce the effectiveness of progestins, leading to a higher risk of unplanned pregnancy if they are being used for birth control purposes.
7. Over-the-counter Remedies Interactions
Drug safety in menopause is essential, as many women use over-the-counter (OTC) remedies to alleviate menopause symptoms like hot flashes, mood swings, and sleep disturbances. Common OTC remedies include herbal supplements, vitamins, and natural treatments. These can interact with prescription medications as well:
- Herbal Supplements (e.g., Black Cohosh, Soy Isoflavones): While often used for symptom relief, these can interact with medications like blood thinners, antidepressants, or hormone therapies. For example, soy-based supplements may interfere with estrogen-based therapies, leading to hormonal imbalances.
- Vitamin Supplements (e.g., Vitamin E, Vitamin D): High doses of vitamin E may increase the risk of bleeding when taken with blood thinners. Vitamin D, often used to support bone health, can interact with certain medications, like corticosteroids or anticonvulsants, affecting calcium and bone metabolism.
Always inform your physician about all the medications you’re taking to avoid potential interactions and enhance drug safety during menopause. Staying proactive and informed about possible drug interactions helps you make the best decisions for your health and prevents complications during this important phase of life. Remember, your health is worth the extra care!
In a nutshell, Menopause is a significant milestone that brings physical and emotional changes. While these changes can be challenging, understanding drug safety and medication options can empower you to manage symptoms effectively. From hormone replacement therapy to natural remedies, your journey can be supported with the right choices and proper medical guidance.
Take the time to consult your healthcare provider, stay informed about possible drug interactions, and follow prescribed treatment plans diligently. By doing so, you can enhance your quality of life during menopause and beyond. For convenient access to medications tailored to your needs, trust Stadium Pharmacy. Whether you need pharmacists consultation or home delivery, we’ve got you covered. Call us at 816-356-4600 and order your meds today for reliable and efficient drug safety in menopause!

